Along with the tremendous benefits of cloud computing technologies, organizations
and businesses in China are faced with a rapidly evolving digital threat
landscape. A Mozilla survey of the top 1 million websites in June 2017 shows a
staggering 93.45% earned an F for failure to implement basic measures that
would protect them from common attack methods. From now and then, company names
appear in news headlines for being hit by serious data hacks which force their
business offline or even result in great revenue loss and reputation damage.
Deploying a Web Application Firewall (WAF) as the front line to stop attacks from taking place should be a necessary preventive and detective measure for any organization or business wishing to protect their treasured data.
A web application firewall (WAF) is an application firewall for HTTP applications, which applies a set of rules to an HTTP conversation. Generally, these rules cover common attacks such as cross-site scripting (XSS), SQL injection, and application-layer denial of service (DoS), which can lead to data deletion, data change (like replacing prices with wrong prices) or data theft. While a classic firewall is the protection on the NETWORK LAYER, a WAF is the protection on the APPLICATION LAYER from Users to Servers.
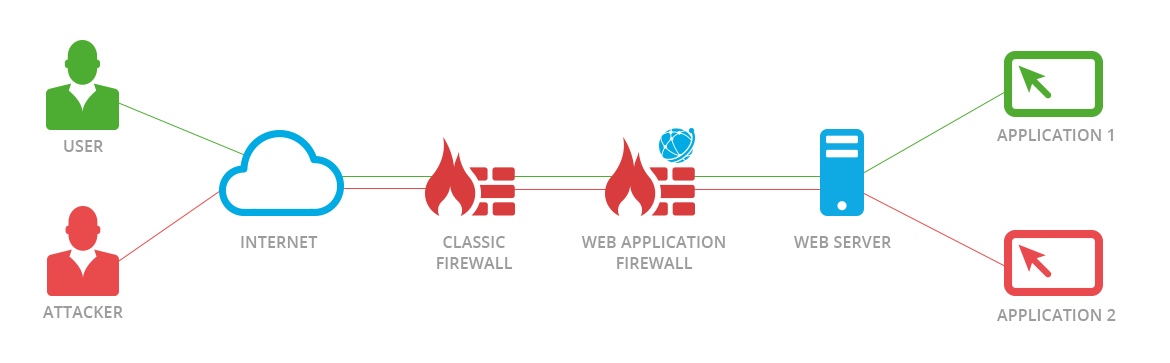
Usually, there are three common ways to deploy a WAF, that is,
hardware-based, software-based and cloud-based solutions, each with advantages
and shortcomings. You can select one or make a combination based on your
compliance needs and budget.
A WAF, if deployed well, will definitely serve as an effective security control for web applications. Nevertheless, under no circumstance should a WAF be regarded as a one-for-all solution against all web attacks as in this fast changing digitally connected world where web applications are constantly developing and innovative attacks come springing up. In the next few articles, more security control methods that complement WAF will be introduced.