Nowadays
in China, companies’ operation is closely related to data storage and management.
Servers and data centers store and process large amount of data every second. Loss
of system resources or data, which may happen from time to time due to any failure.
A failure may be caused by small equipment problems or large-scale natural disasters
such as earthquakes, fires, flood and typhoon or other unexpected incidents. 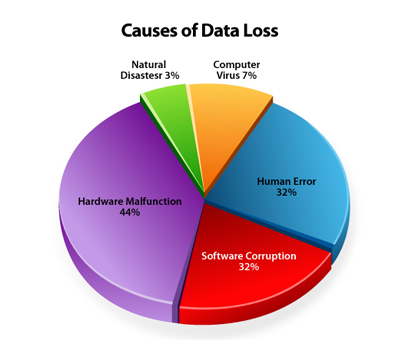
Companies
develop business continuity plans to minimize any event that might negatively
impact operations. A business continuity plan (BCP) is a plan to help ensure
that business processes can continue during a time of emergency or disaster,
which usually includes a range of disaster scenarios and the steps that a
company or organization should take in those particular scenarios to resume
normal operation. To establish a BCP, impact analysis, business impact analysis
(BIA), threat and risk analysis (TRA) and impact scenarios should first be
considered. In this process, it is important to determine critical functions
and assign the following two values:
Data backup can be deemed as a simple form of disaster recovery plans and is an efficient and economical way for businesses to recover their data after a disaster. Actually, backup can be deemed as part of the foundation of any disaster recovery plan.
The
backup process is the copying into an archive file of data in case it might be
used to recover the original in the event of data loss. Companies can choose a
most suitable data storage medium according to their particular set of
circumstances, for example, magnetic tape, hard disk, recordable CDs, DVDs, fresh
memory, as well as remote backup and cloud backup services. And there are also
various data repository models to choose from.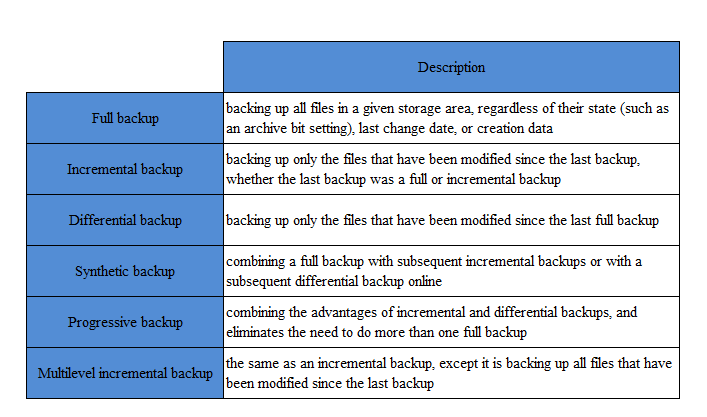
Regularly, backup involves the following steps: